Navigating the world of insurance can be challenging for the owner of a trucking business. It is crucial to understand the differences between admitted insurance, non-admitted insurance, captive insurance, and risk retention groups (RRGs) in order to make informed decisions on the insurance policy so that it addresses business needs.
All of the insurance company types mentioned above have their advantages for specific scenarios and operate under their specific regulatory frameworks. Knowing all the options available allows you to choose cost-effective and best-fit insurance coverage that will protect your trucking business in the time of need.
Admitted vs. Non-Admitted Insurance: What’s the Difference?
Admitted Insurance
An admitted insurance company is licensed and regulated by the state’s department of insurance. Insurers admitted to operating in the market must follow strict regulations and financial stability checks combined with standardized policy definitions and protective measures for policyholders. Policyholders who trust an admitted insurance company gain additional security as the state’s guarantee fund ensures the claims are paid even if the insurance carrier becomes insolvent.
Advantages of Admitted Insurance:
- State regulation ensures that policies meet minimum coverage standards.
- Policyholders can access a state-backed guaranty fund if the insurer becomes insolvent.
- Often more affordable due to state oversight and standardized pricing.
- Greater consumer protection, ensuring reliable coverage and fair claims processing.
Disadvantages of Admitted Insurance:
- Less flexibility in policy customization.
- The approval process for new policies and rates can be slower due to regulatory oversight.
- Limited options for high-risk trucking operations that may need specialized coverage.
Non-Admitted Insurance
Non-admitted insurance provides coverage to clients despite lacking state licensing. As non-admitted insurance carriers are not under the same regulatory constraints as admitted insurance companies, there is an additional level of flexibility for underwriting decisions. Sometimes referred to as surplus lines carriers, those insurance companies provide coverage to businesses that cannot obtain insurance through admitted carriers due to unique high risks. However, it doesn’t mean their policies are not valid.
Advantages of Non-Admitted Insurance:
- Provides coverage for unique or high-risk operations that admitted insurers may not cover.
- Insurance policies can be customized to meet specific business needs.
- Faster approval process for policy changes and adjustments.
- Available options for trucking companies that operate across multiple states with varying regulations.
Disadvantages of Non-Admitted Insurance:
- No state guarantee fund protection.
- Premiums tend to be higher due to increased risk factors.
- Weaker regulatory oversight may produce various interpretations of policies when organizations fail to follow rules.
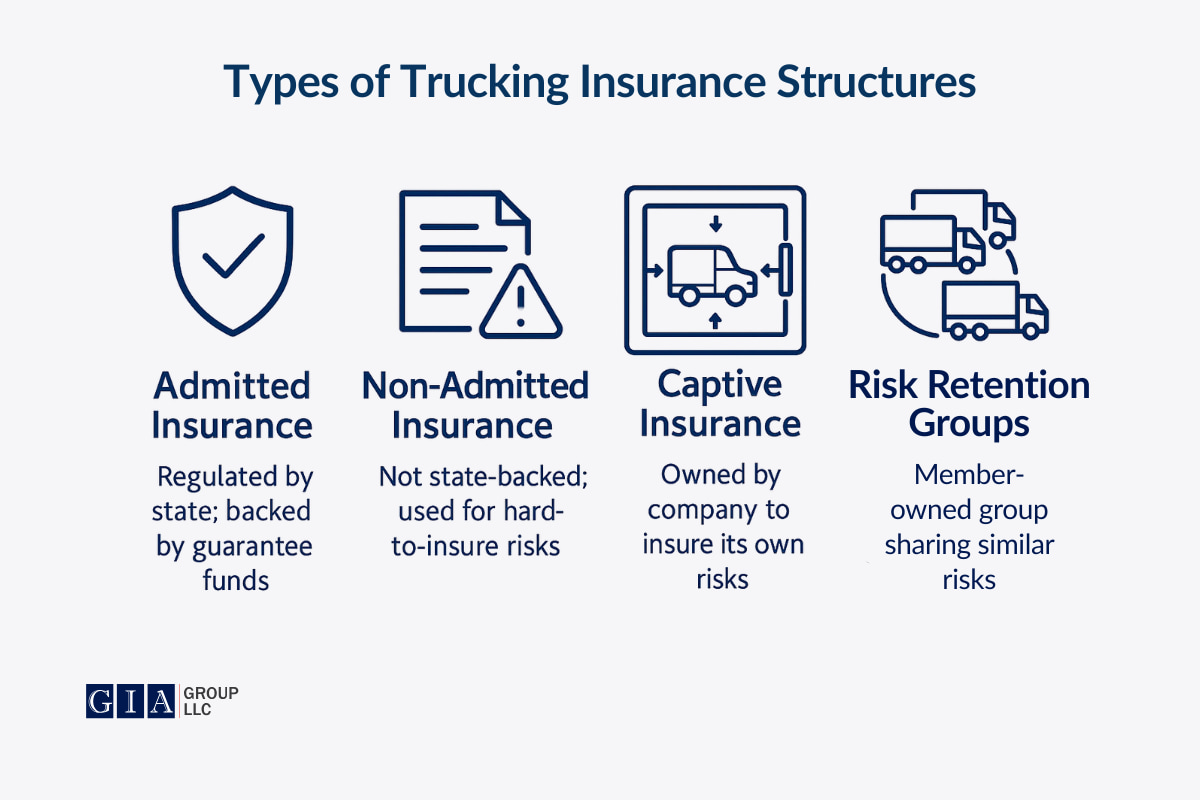
Captive Insurance: Taking Control of Your Coverage
Captive insurance companies are licensed insurance companies formed by a business or a group of businesses to address their specific risks. This form of an insurance company encourages better risk practices, as one of the main benefits to insureds is that a reduction in claims amount and cost has a positive impact on a trucking business’s bottom line.
Why Consider Captive Insurance?
- By self-insuring (instead of paying a premium to another insurer), trucking companies can save on insurance costs if they have lower claim rates.
- Policyholders have more control over the various types of risks they would like to insure.
Potential Downsides:
- Establishing a captive requires significant upfront capital and administrative costs.
- Running an insurance company requires expertise, compliance with regulations, and ongoing financial oversight.
- If claims exceed expectations, captive members bear the responsibility for covering costs.
Risk Retention Groups (RRGs) as a Group-Based Insurance Alternative
The Liability Risk Retention Act of 1986 established Risk Retention Groups (RRGs) as unique insurance entities that operate as liability companies and are owned by their policyholders. Since trucking companies pull together their resources and become owners of an RRG, they both take part in risk sharing and profit distribution.
Benefits of Joining an RRG:
- Policyholders in member-controlled groups can influence operations and company-wide decisions.
- Adhering to fewer state regulations enables RRGs to minimize expenses, thus lowering their costs.
- There are great direct financial benefits from maintaining safe operations if you are a member of an RRG.
Downsides to Consider:
- Not all types of risks can be covered by an RRG.
- If claims exceed expectations, members could be required to contribute additional funds.
How to Choose the Right Insurance for Your Trucking Business?
- So how do you decide which insurance type best fits your trucking company? Ask yourself:
- Do I want the security of state-backed protection?
- Do I need tailored coverage for a unique high risk?
- Am I interested in lowering long-term costs and having more control?
- Would I benefit from being part of a member-controlled insurance program?
- Which of these factors is predominant for my business operations?
Conclusion
Different types of insurance will work differently for your specific business, depending on your organizational structure, financial capacity, and risk-bearing capability. Trucking companies use a combination of various insurance types to obtain essential protection through balanced costs. The crucial factor involves a thorough examination of available choices followed by an analysis of potential risks along with their advantages.
Understanding the differences between admitted and non-admitted insurance, captive insurance, and RRGs will help you make the right choice. It’s best to consult truck insurance specialists.
